Antiseptics and flame retardants: the choice of protective impregnation for application on a wooden floor
Despite the emergence of new flooring, wooden floors are still at their peak. They are environmentally friendly, distinguished by their beauty and practicality. However, wood, as a building material, is not without drawbacks. Bark beetles, fungi, various pathogenic microorganisms like to settle in it. Under the influence of moisture, the wood swells and cracks, and high temperatures can cause it to ignite. Fortunately, all these shortcomings can be eliminated. For this, there are special protective impregnations that can increase the durability of wooden coatings several times. The main thing is to choose a composition with the desired properties, and then - correctly apply it on a wooden surface.
Impregnation is a composition that performs a number of protective functions. Depending on the purpose, antiseptics, flame retardants and combined formulations are distinguished among them.
Content
Antiseptics - protection against microorganisms
Antiseptics prevent the destructive effects of insects, fungi, viruses, putrefactors and other pests on wood. Often, substances that protect the wooden surface from ultraviolet radiation and atmospheric precipitation are often introduced into the composition of antiseptics for outdoor work. It is important to pay attention to this when choosing an antiseptic for flooring a veranda or terrace.
Many modern antiseptics have water repellent properties. This eliminates the possibility of warping, cracking and torsion of the elements of the wooden floor with prolonged exposure to moisture.
Antiseptics can be prophylactic or therapeutic.
Preventive formulations represent the bulk of antiseptics. They process undamaged wood - for its subsequent protection during operation. A popular representative of such antiseptics is Neomid 400, which forms a colorless film on a wooden surface that does not allow insects and bacteria to enter the tissues.
Therapeutic antiseptics contain more aggressive components that not only scare away, but also destroy wood pests. These products are used on wooden surfaces that have already been subjected to destructive effects. Or where difficult operating conditions exist. For example, on wooden floors in bathhouses, where high humidity initially increases the risk of rotting. Here therapeutic antiseptics, for reinsurance, are often used as preventive.
The therapeutic composition of Neomid 100 Antizhuk, which has a detrimental effect on bark beetles, shashels and other insect pests, has proven itself perfectly. A similar effect has the antiseptic Wood healer DL-2.
Fire retardants - fire protection
Impregnation-flame retardants protect wood from thermal destruction, that is, from ignition under the influence of heat or fire. Chemicals that are part of flame retardants, at high temperatures, create compounds that prevent fire or the spread of flame. Naturally, flame retardants are not a complete fire guarantee.They allow wooden surfaces to resist thermal aggression, but only for a short time (about 10-15 minutes when heated to 700˚C).
Fire retardants are recommended to be used to protect wooden floors in rooms where an ignition source is installed - a stove, fireplace, etc.
According to the mode of action, fire-retardants are divided into 2 groups. The first includes flame retardants that prevent combustion. To the second - blocking the spread of fire.
Fire retardants, during an increase in temperature, begin to emit non-combustible gases. They push air away from the surface of the wood and thereby make burning impossible.
Blocking flame retardants form a special film on the wood surface. When exposed to fire, this film swells and blocks the access of oxygen (necessary for combustion) to the protected surface.
On top of flame retardants, paints, primers, varnishes, plasters, etc. can be applied. Often fireproofing is used in tandem with antiseptics. For best results, it is recommended that you first apply a layer of antiseptic to the surface, then a flame retardant. For example, you can use this scheme: the first 2-3 layers - Neomid 400 antiseptic, the next 2-3 layers - Neomid 530 fire protection.
Combined impregnation - two in one
If it is necessary to protect the surface of a wooden floor from fire and biological pests at the same time, it is easier to use combined impregnations. They include both flame retardants and antiseptics. Among such means: Senezh Ognebio, Neomid 450, Bioneutral W 31, BS-13.
Particular attention to the composition!
The quality of the impregnation and its functional properties are significantly dependent on the composition. Protective preparations can be made on the basis of water, oils and organic solvents. What is the difference?
Water-soluble compounds are liquid impregnations that are deeply absorbed into the structure of wood. They are easy to apply to the surface with a brush or spray; the drying time is 2-3 hours. They have low toxicity, are odorless and are excellent for processing floors inside residential premises. Both antiseptics and flame retardants can be water soluble.
An important feature: some water-soluble compounds are easily washed with water. Therefore, in wet rooms, it is recommended to apply film-forming varnishes or paints on top of such compositions. Elements in contact with water are not treated with water-washable impregnations.
Oil impregnation - thick oils that create a dense film on the treated surface. They are highly flammable, but protect wood for a long time from insects, rot, fungi. Some of the oil formulations are toxic and have a heavy odor, therefore they are used only for external treatment. The drying time of the oil-based composition is about 4 hours. Oil impregnations are applied on their own, without finishing coloring with varnishes and paints.
Oily water-soluble compounds are found on the market. They are low toxic, they are used both outdoors and indoors. Unlike oils, they can be painted with finishing paints and varnishes.
Impregnation based on volatile organic solvents is another group of compounds that have water repellent properties, protect the wooden surface from house fungus, mold, insects. Such compositions are easy to apply, but dry for a long time - about 12-24 hours. With their help, wood can be given a very deep, saturated shade.
Decorative properties of impregnation
Impregnations are available transparent or tinted (in accordance with the line of tones of the manufacturer). Only antiseptics have a decorative effect. Completely transparent (colorless) antiseptics perform an exclusively protective function, without changing the natural color of wood. The maximum that they are capable of in decorative terms is to emphasize the structure of the wooden coating. A similar composition is the antiseptic Tikkurila Pinja W-Oil. It is absolutely colorless, but is easily tinted in any of the tones of the Tikkurila line.
Tinted antiseptics are painted initially. They are either available in a specific color scheme, or tinted upon sale, according to the color map proposed by the manufacturer. Such impregnations simultaneously play a protective and decorative role. That is, they can replace other coloring materials: primers, stains, paints, varnishes. A well-known similar antiseptic is Pinotex Classic, its color map includes 10 primary tones and 20 additional ones. In addition, the composition of Pinotex Classic allows you to get many other tones, mixing existing shades in different proportions.
But what about flame retardants? Most of them are colorless and are not noticeable after drying. Others are painted pink or red, which plays not a decorative, but a controlling role. Applying color impregnation on a wooden surface, it is easier to monitor the quality of staining and the absence of gaps.
In addition to everything indicated, when choosing an impregnation, pay attention to:
- Safety. Read the composition on the product label. Make sure that no highly toxic compounds are used in the manufacture of antiseptics (flame retardants): arsenic, pentachlorophenol, fluorine compounds, heavy metal salts.
- Term fire and bioprotection. Fire retardants act on the treated surface for up to 7-15 years, antiseptics - up to 10-20 years.
- The manufacturer. Well-known impregnating compounds with a quality certificate and appreciated by consumers are produced under the brands: Pinotex (Finland), Tikkurila (Finland), Neomid (Russia), Senezh (Russia), Belinka (Slovenia).
Rules for applying protective compounds
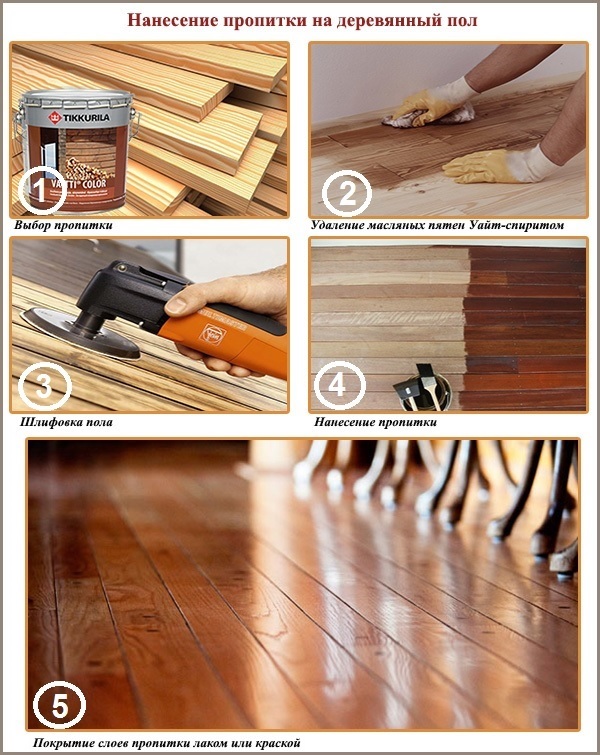
Even the best antiseptic or flame retardant applied “through the sleeves” will not produce the desired effect. In order for the protective properties guaranteed on the label by the manufacturer to fully manifest themselves, you need to adhere to the rules for applying impregnations. Follow the pattern:
Stage # 1 - Wood Drying
The best protection effect is achieved by impregnation on wood whose moisture content does not exceed 20%. The drier the wood, the more protective it can absorb. And, on the contrary, moist wood will not allow impregnation in its pores, the protective layer will be of poor quality. A similar effect will be especially noticeable when using impregnations based on organic solvents and oils.
To achieve the required humidity, the wood is dried in a shady, dry place. Best of all - under a canopy in the yard.
Stage # 2 - surface cleansing
Ready for impregnation, the wooden surface should be clean, uniform, without any signs of early staining. Contaminated areas lead to a deterioration in the absorption of the protective composition and to a heterogeneous, spotty color (if there is color).
If the surface has already been painted, paint or varnish is removed using a building hair dryer. The remaining coating is cleaned with a scraper and a stiff brush. All oily, greasy stains are washed off with white spirit.
Sand is cleaned with sandpaper or a grinder, dust is blown away with a vacuum cleaner.
Stage # 3 - impregnation
Impregnation is applied to the surface with a wide brush, roller, spray. To achieve maximum effect, applying several layers of the drug is required - usually 2-4. Depending on the composition of a particular impregnation, each subsequent layer is applied after complete or partial drying of the previous one (specify this point in the instructions!). The time interval between application of the layers can be from 1-2 to 24 hours.
The dried impregnation layer is sanded with sandpaper or a grinder to smooth out the raised pile of wood. After - cover the surface with varnish or paint, which enhance the decorative and protective effects of the coating.
A detailed description and a visual demonstration of the process of treating wood with impregnations will help you conduct this procedure correctly. Watch the video:









3 comments