What appliances in the house consume the most electricity
The most stable thing in our life is the increase in utility bills. Let's look at the “contribution” made by various household appliances to the monthly electricity bill.
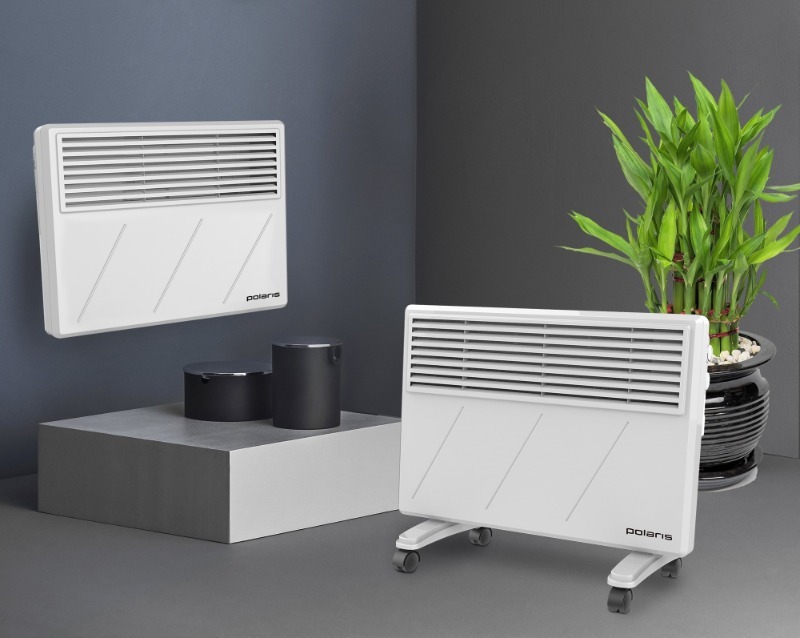
Heater
The electric heater perfectly helps us out in conditions of an insufficiently comfortable room temperature. The energy consumption of this household appliance directly depends on its type. For example, convector heaters consume up to 1.5 kW / h, and oil models over 1 kW / h.
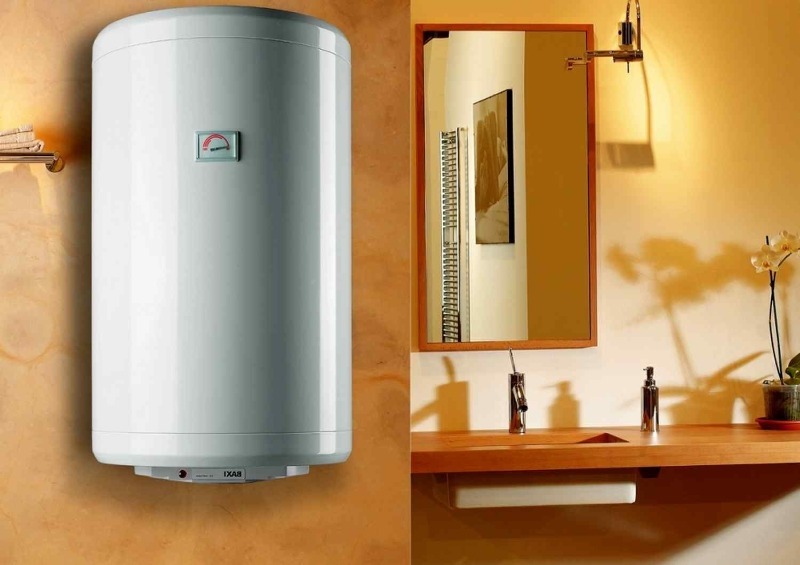
Water heater
The main advantage and advantage of a water heater is its independence from the central hot water supply system. The following indicators can affect the consumption of energy: the type of device and its power, tank volume. In most cases, storage-cycle water heaters consume about 2 kW of electricity for each hour of their operation. The power consumption for flow-type water heaters ranges from 3 to 27 kW, depending on the model.
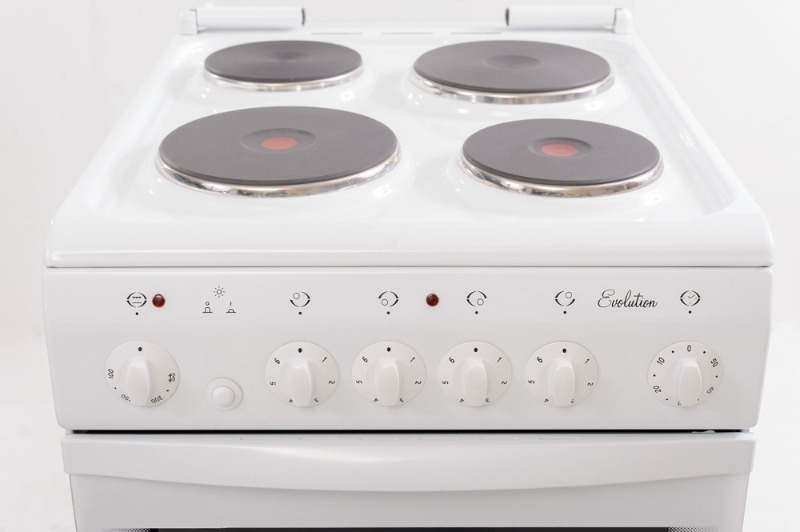
Electric stove
Depending on the chosen model and energy class, a conventional four-burner stove consumes from 4 to 8 kW per hour. However, we very rarely turn on all burners at the same time, so the actual energy consumption is always much less.
Air conditioning
The energy consumption of the air conditioner depends on many factors (weather conditions, power, its type, room area). Systems with high cold productivity have a high level of power consumption, reaching 3.5 kW. To save energy, an inverter compressor control system has been developed that helps save up to 50% of electricity.
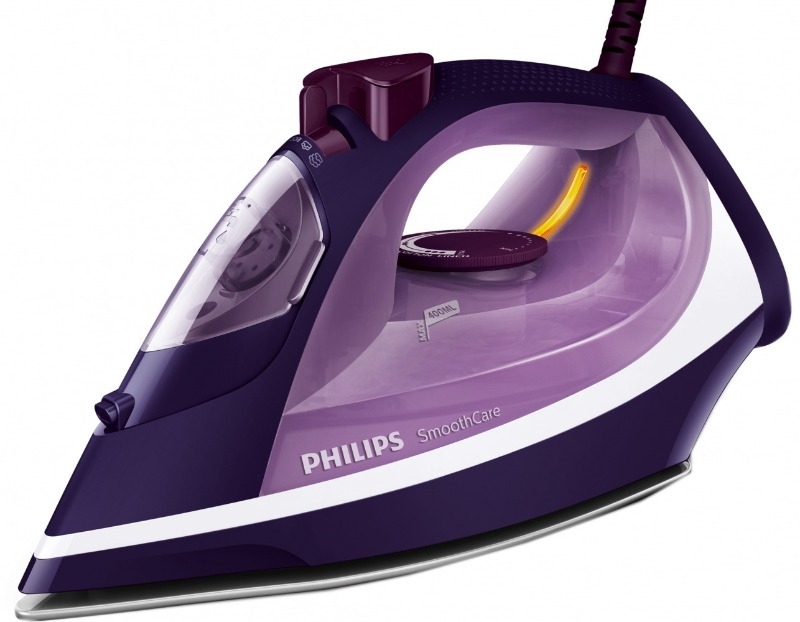
Iron
It is the "record holder" in energy consumption among all other appliances of household appliances. It consumes from 1.5 to 3 kW per hour of operation.
Washer
The maximum power of modern models of washing machines is 1.8-2.5 kW. In fairness, it is worth noting that the home assistant consumes so much energy only in the "boiling" mode. When washing in other modes, the cost of electricity is much less. Therefore, in order to save, it is desirable to choose the shortest and lowest temperature programs.
Refrigerator
The capacity of new generation refrigerators varies from 100 to 200 watts per hour. This is the average power consumption in compressor operation mode. It should be borne in mind that the active operation of the engine ends when a sensor signal is received to achieve the required temperature. In the summer, for high-quality cooling of products, more frequent inclusions are necessary. Therefore, it turns out that the energy consumption directly depends on both the established temperature regime of the device itself and the ambient temperature.
Electric kettle
The electric kettle has an electric power consumption similar to that of an iron. But, unlike the same refrigerators and computers, we use kettles and irons for only a few minutes, which makes their overall cost in terms of power consumption not too noticeable for our wallet.
A vacuum cleaner
The consumption of electricity by these "helpers", responsible for cleanliness in the house, varies between 1.5-3.0 kW per hour, which depends on the specific model.
Microwave
Depending on the power, the microwave consumes from 0.7-1.2 kW per hour.A microwave left in standby mode consumes up to 3 watts per hour, which allows this device to “add” a couple more kilowatts to your monthly electricity bill.
Personal Computer
The power consumption of a personal computer consists of several factors:
- Power supply unit. It is directly related to processor performance and the features that may be available to the user. The average representative of this segment power is about 400 watts.
- Monitor power. It depends on the size of its diagonal and the parameters of sound and color, as well as energy consumption in standby mode.
TV
The power of modern TVs with a LED tube is directly dependent on the size of the screen itself. The larger it is, the more energy consuming for the consumer. Of course, the screen and sound settings affect, but these factors do not play a significant role in the issue of energy saving. 32-inch LED-TV, depending on the set of additional functions, consumes 40-55 watts during one-hour operation and 0.5 watts at the same time in standby mode. 15-20% more electricity is consumed by televisions with high definition images and color reproduction quality, the so-called "plasma". In this case, unlike its LED counterparts, the option of changing the picture quality settings can very much affect the power consumption. Bulky and not ideal in terms of playback TVs of the old model with a cathode ray tube can “eat” up to 155 kW per hour.
Hair dryer
An ordinary household hair dryer has a power of 1200 to 1800 watts, this is enough to create a strong stream of heated air and dry your hair quickly enough. The power of professional models exceeds 2100 W, which makes their use at home economically unjustified.